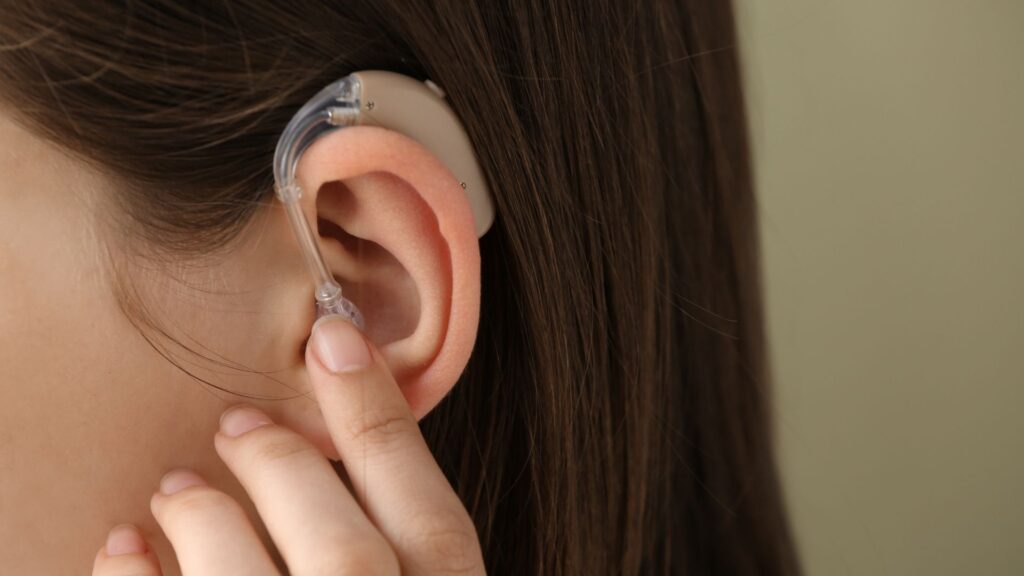
While most people have never heard of them, over-the-counter (or OTC) hearing aids are actually quite useful for some people. They do not require a prescription or professional installation and can be purchased at many stores, online sites, or even at your audiologist’s office.
OTC hearing aids usually contain digital technology and work by amplifying sounds you want to hear better. These can include things like conversations in the surrounding area or footsteps outside your door. But how well they do this can vary, and we still don’t know how they will perform compared to conventional hearing aids.
Why are over-the-counter hearing aids popular?
Many people choose to purchase their own personal, private hearing aid without professional assistance due to several reasons. Some feel that they do not have enough money for a professionally fitted one or cannot afford to make the necessary appointments needed to get them. Others believe that their hearing is not bad enough to warrant conventional hearing aids, which are intended to be worn all day. Whatever the reason, it’s important that you find something that works best for you. And if that’s over-the-counter hearing aids, we can help you with those.
What should you look for when buying an over-the-counter hearing aid?
The price of most hearing aids, both conventional and OTC, is determined by two main factors: (1) how much technology they have built in; and (2) and what kind of case they are in.
The more advanced the features, like voice recognition or digital noise reduction, the higher the cost. Similarly, if they use earmolds that must be custom made, this can also add to the expense. Additionally, you may want help setting up your OTC hearing aids if you’re uncomfortable doing it yourself. You audiologist can usually help you with this for a small fee.
How can you get a hearing test?
Most health care professionals conduct basic hearing tests in their clinics or facilities, but for the most accurate results you’ll want to see a licensed audiologist with properly calibrated equipment in a sound-controlled environment.
The doctor will play sounds at different pitches to find the softest sounds that you can hear in the range of frequencies that make up speech. Your scores, called puretone thresholds, indicate the severity and configuration of your hearing loss. They are plotted on a graph called an audiogram.
Whether you decide to get conventional hearing aids or OTCs, it’s important to have a proper audiogram collected. It will help determine whether there are any other health concerns like an acoustic neuroma, or whether you can expect to get benefit from hearing aids. Or whether your hearing loss could be improved with medical treatment.
What effects do hearing aids have?
The simplest function of hearing aids is that they boost certain sounds to help you hear better. They do a lot more than that, with modern digital processing, but that’s basically their primary function. The effect is not to improve your hearing, but rather to make it easier for you to understand. Both OTC and conventional hearing aids will make sounds louder to help you understand better. But they accomplish this goal in different ways.
Conventional hearing aids are selected with professional help from your audiologist and adjusted according to your needs. Ideally, they are fit to amplification targets using real-ear verification. But then you also return to that audiologist for follow-up adjustments to get them tuned in to what sounds best to you.
OTC hearing aids are fit independently. You pick out your hearing aids. You do the programming and the troubleshooting and adjusting. Your audiologist can help a little bit, but our options are pretty limited.
How can you choose the right hearing aid?
I like to think of this question as being similar to asking how to choose the right car. There are lots of different things to consider, but when it comes down to it, the device has one primary function that is going to work no matter which one you get. There are differences in the way the devices process sounds, especially in noisy environments, and you might prefer the sound quality of one over others. But they will all help you understand better.
Luckily, your audiologist knows how to help you make the right choice. They’ll discuss what your typical listening environments are like. They’ll take a look at your goals for understanding. And they’ll even make sure that the hearing aids will be compatible with your phone.
If you’re trying to decide between OTC hearing aids or conventional ones, you need to ask yourself whether you will be wearing them all day and whether you’re comfortable setting them up yourself. If you’re only going to wear them in certain situations, OTC might be better for you. But if you plan to use them more consistently, or if you think you’ll have problems doing your own setup, then you might like conventional hearing aids better.
What should you do after buying a hearing aid?
Use them as much as you can! You will have a trial period to make sure you’re happy with them. So you should take full advantage of that period by using them in lots of different situations. If you decided on OTC hearing aids, there’s really not much to do regarding follow-up. You’re responsible for your own maintenance and adjustments. But if you got conventional hearing aids, your audiologist might have you come back in a few weeks to check in and adjust the sound or physical fit.
Can you get OTC hearing aids at Link Audiology?

Yes, you can! We currently offer the Jabra Enhance Plus. You will need to have an iPhone to use them. But we can also help you set them up for a small fee if you aren’t comfortable doing it yourself. Call us today to schedule an appointment!

